Parabolic Path Of Satellite

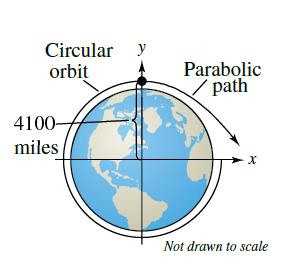
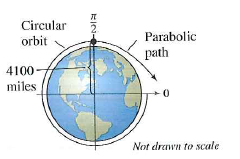
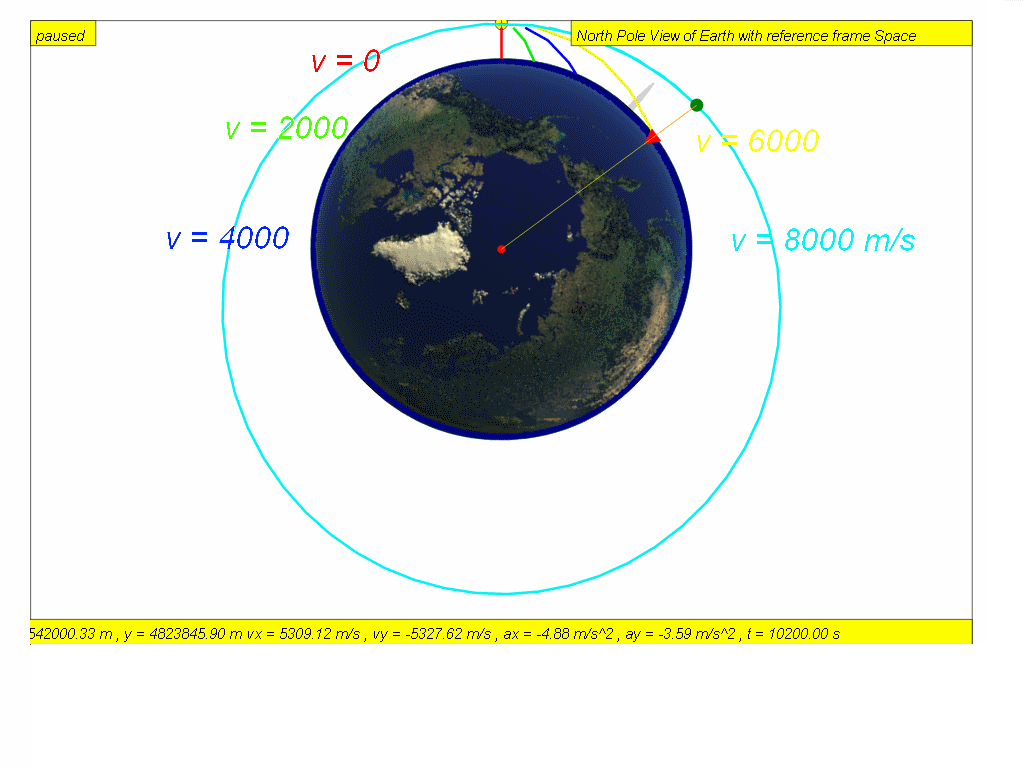
The type of path that will be taken up by an unpowered space vehicle starting at a given location will depend upon its velocity.
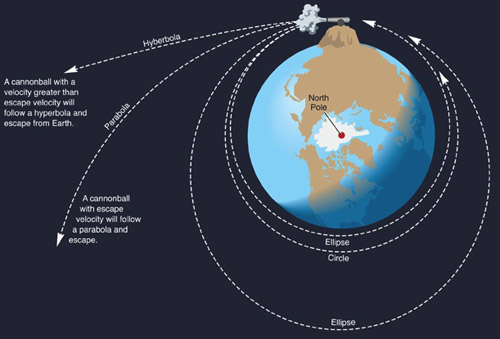
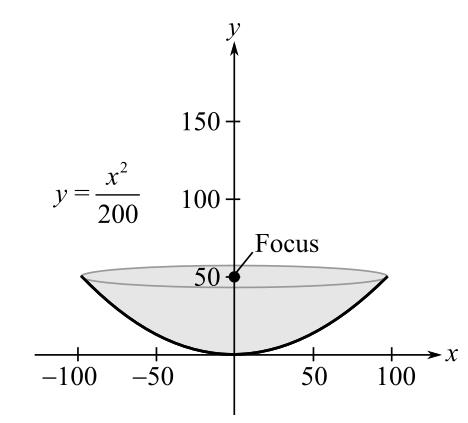
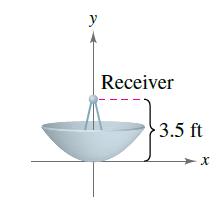
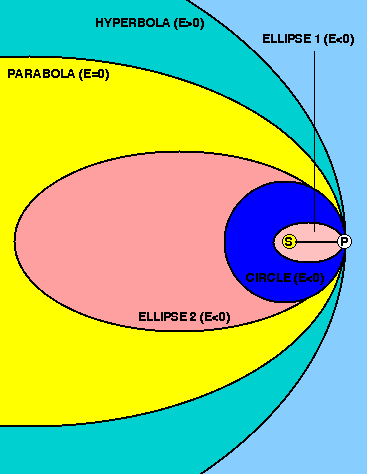
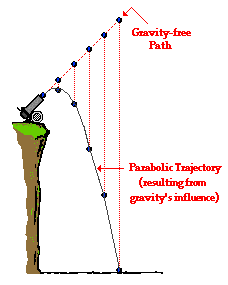
Parabolic path of satellite. An object travels in a parabolic path when it is under the effect of an accelerating force which is always pointing along the plane of the motion of the object. In classical mechanics a trajectory is defined by hamiltonian mechanics via canonical coordinates. A parabolic antenna is an antenna that uses a parabolic reflector a curved surface with the cross sectional shape of a parabola to direct the radio waves the most common form is shaped like a dish and is popularly called a dish antenna or parabolic dish the main advantage of a parabolic antenna is that it has high directivity it functions similarly to a searchlight or flashlight reflector to. The green path in this image is an example of a parabolic trajectory.
Escape velocity is by definition that velocity required at a given location to establish a parabolic orbit. A parabolic trajectory is depicted in the bottom left quadrant of this diagram where the gravitational potential well of the central mass shows potential energy and the kinetic energy of the parabolic trajectory is shown in red. A trajectory or flight path is the path that an object with mass in motion follows through space as a function of time. Hence a complete trajectory is defined by position and momentum simultaneously trajectory in quantum mechanics is not defined due to heisenberg uncertainty principle that.
It will take up an open ended path if its velocity equals or exceeds escape velocity.